Table of Contents
- Cirrhosis of the Liver: Understanding the Silent Killer
Cirrhosis of the Liver: Understanding the Silent Killer
Cirrhosis of the liver, often referred to as the silent killer, is a complex and progressive liver disease characterized by the gradual replacement of healthy liver tissue with scar tissue. This process ultimately impairs the liver’s ability to perform its vital functions effectively. Over time, the accumulation of scar tissue can lead to significant deterioration in liver function and an increased risk of developing life-threatening complications. It’s imperative to recognize the seriousness of this condition and seek timely medical intervention to manage symptoms and prevent further progression. Understanding the silent threat of Cirrhosis of the Liver is crucial for early detection and treatment.
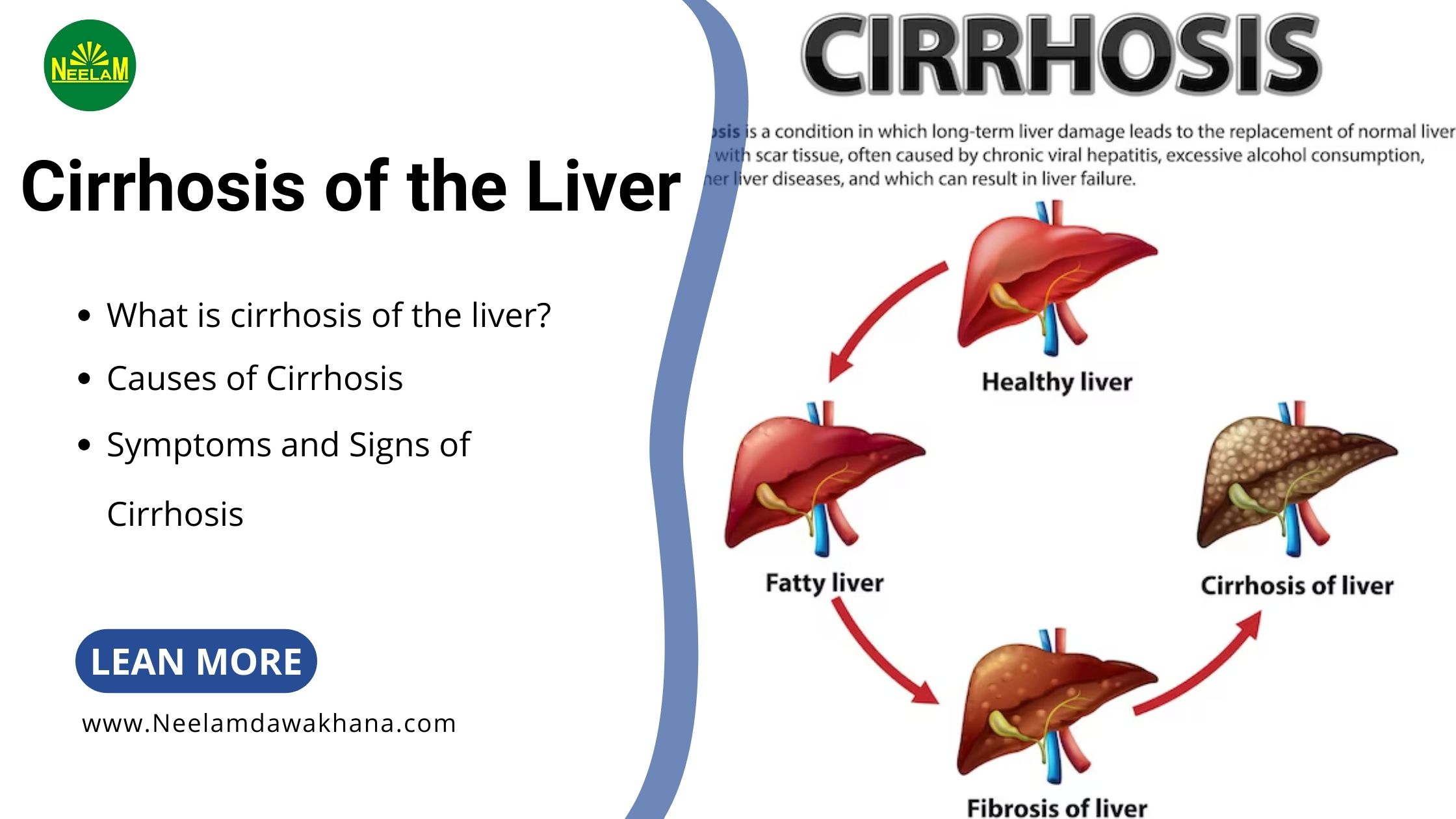
What is cirrhosis of the liver?
Cirrhosis of the liver, often dubbed the silent killer, is a chronic condition where healthy liver tissue is gradually replaced by scar tissue, impairing liver function. It’s often caused by factors like excessive alcohol consumption, chronic viral infections (hepatitis B and C), or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Symptoms of this silent killer include fatigue, jaundice, abdominal pain, and swelling. Diagnosis involves thorough medical history, physical exams, and various tests. Treatment strategies for Cirrhosis of the Liver: Understanding the Silent Killer focus on managing symptoms, preventing complications, and may involve lifestyle changes or, in severe cases, liver transplantation. Preventive measures include limiting alcohol intake and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
How does cirrhosis effect my body and liver?
Cirrhosis affects the liver and body by:
- Impairing liver function due to scar tissue buildup.
- Increasing pressure in the portal vein, leading to complications like varices and ascites.
- Decreasing blood clotting ability, causing easy bruising and bleeding.
- Resulting in jaundice due to bilirubin buildup.
- Triggering confusion and coma from toxin buildup (hepatic encephalopathy).
- Raising susceptibility to infections due to compromised immune function. Early diagnosis and management are crucial for minimizing complications and improving quality of life.
Causes of Cirrhosis
Alcohol Consumption
Excessive alcohol consumption over an extended duration stands as a primary contributor to cirrhosis, a severe liver condition. The intake of alcohol inflicts harm upon liver cells, instigating inflammation and subsequent scarring, which exacerbate the progression of cirrhosis.
Hepatitis B and C
Chronic viral infections like hepatitis B and hepatitis C have the potential to induce inflammation and inflict damage upon the liver. Left untreated, these infections can progress to cirrhosis, a severe condition characterized by irreversible liver damage and scarring.
Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD, or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, manifests as a condition marked by the accumulation of fat within the liver. Particularly in individuals grappling with obesity or diabetes, NAFLD poses the risk of progressing to cirrhosis, highlighting the gravity of the condition and its potential complications.
Symptoms and Signs of Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis often progresses slowly, and symptoms may not be noticeable in the early stages. However, as the disease advances, individuals may experience:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Abdominal pain and swelling
- Easy bruising and bleeding
Complications of Cirrhosis
Portal Hypertension
When the liver undergoes scarring, it can impede the flow of blood through its vessels, consequently elevating pressure within the portal vein—a condition known as portal hypertension. Such an occurrence can pave the way for severe complications like variceal bleeding and ascites, underscoring the critical nature of liver health and the implications of its impairment.
Ascites
Ascites denote the accumulation of fluid within the abdominal cavity, resulting in swelling and discomfort. Moreover, it heightens the susceptibility to infections, accentuating the urgency of addressing this condition promptly.
Hepatic Encephalopathy
Hepatic encephalopathy is a complex condition marked by cognitive impairment and confusion. It arises due to the liver’s diminished capacity to efficiently eliminate toxins from the bloodstream. As these toxins accumulate, they affect brain function, leading to a range of symptoms, including altered mental states, difficulty concentrating, and in severe cases, even coma. Understanding the intricacies of this process emphasizes the critical need for managing liver health and addressing hepatic encephalopathy promptly to mitigate its impact on overall cognitive function and well-being.
Diagnosis of Cirrhosis
Diagnosing cirrhosis, particularly within the framework of understanding the silent killer, typically necessitates a comprehensive approach. This includes evaluating medical history, conducting physical examinations, administering blood tests, and utilizing imaging studies like ultrasound or MRI. Additionally, in some cases, a liver biopsy may be required to confirm the diagnosis. It’s crucial to recognize the gravity of Cirrhosis of the Liver Understanding the Silent Killer and employ thorough diagnostic methods to ensure timely intervention and management of this silent threat.
Treatment Options for Cirrhosis
While there is no cure for cirrhosis, treatment aims to slow disease progression, manage symptoms, and prevent complications. Treatment options may include:
- Lifestyle changes (such as abstaining from alcohol and maintaining a healthy diet)
- Medications to manage symptoms and complications
- Liver transplantation for advanced cases
Preventive Measures for Cirrhosis
Preventing cirrhosis involves adopting healthy lifestyle habits and minimizing risk factors:
- Limiting alcohol consumption
- Getting vaccinated for hepatitis B
- Maintaining a healthy weight and diet
- Regular exercise and physical activity
Which conditions have certain risk factors?
- Consume excessive alcohol.
- Have chronic viral hepatitis (HBV or HCV).
- Suffer from non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
- Struggle with obesity.
- Have a family history of liver disease.
- Engage in intravenous drug use.
- Have autoimmune liver diseases.
- Have poorly managed diabetes.
- Experience chronic bile duct obstruction.
Living with Cirrhosis
Managing life with cirrhosis presents its challenges, yet individuals can find support and resources through various support groups. Additionally, adopting dietary adjustments like a low-sodium diet and avoiding specific medications can significantly enhance one’s quality of life amidst this condition.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cirrhosis of the liver stands as a serious condition necessitating early diagnosis and intervention. Through comprehension of its causes, symptoms, and available treatment options, individuals can proactively safeguard their liver health and enhance their overall well-being with resources like Neelam Dawakhana.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q. Is it possible to reverse cirrhosis?
A. While early-stage cirrhosis may be reversible with lifestyle changes and medical treatment, advanced cirrhosis typically cannot be reversed.
Q. How long can you live with cirrhosis?
A. The prognosis for individuals with cirrhosis varies depending on the severity of the condition and the presence of complications. With proper management and treatment, some people can live for many years with cirrhosis.
Q. Is cirrhosis painful?
A. Cirrhosis itself may not cause pain, but individuals with cirrhosis may experience abdominal discomfort due to complications such as ascites or enlarged liver.
Q. Can cirrhosis be prevented?
A. Cirrhosis can be prevented by adopting a healthy lifestyle, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, getting vaccinated for hepatitis, and managing underlying health conditions such as obesity and diabetes.
Q. What foods should be avoided with cirrhosis?
A.Individuals with cirrhosis should avoid foods high in sodium, processed foods, and those that are difficult to digest. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains is recommended.