Table of Contents
- Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Symptoms and Causes
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Symptoms and Causes
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) presents various symptoms and has multiple causes. Symptoms, such as fatigue and abdominal discomfort, often emerge in advanced stages, while causes include sedentary lifestyles, poor diets, obesity, insulin resistance, and genetic factors. Early detection and management are crucial, highlighting the significance of adopting healthier lifestyles and regular medical monitoring.
Introduction to Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is a common condition where excessive fat accumulates in the liver cells, unrelated to alcohol intake. It’s closely linked to obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome. Despite often being asymptomatic initially, NAFLD can lead to serious complications like liver scarring and cardiovascular issues. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and management is vital for addressing this widespread health concern.
Understanding the Causes of NAFLD
Sedentary Lifestyle and Poor Diet
A sedentary lifestyle and poor dietary habits are significant contributors to the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity or regular exercise increases the risk of NAFLD. Sedentary behavior leads to reduced metabolism and inefficient fat utilization by the liver, promoting fat accumulation.
Poor Diet: Consuming a diet high in processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats contributes to NAFLD. Excessive intake of calories, particularly from refined carbohydrates, overwhelms the liver’s capacity to metabolize fats effectively.
Addressing these lifestyle factors through regular physical activity and adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains is crucial for preventing and managing NAFLD effectively.
Obesity and Insulin Resistance
Obesity: Excess body weight, especially abdominal obesity, increases the risk of NAFLD. Fat tissue releases inflammatory substances that can lead to liver inflammation and damage.
Insulin Resistance: Insulin resistance occurs when cells fail to respond properly to insulin, leading to high levels of insulin in the blood. This promotes fat accumulation in the liver and contributes to the progression of NAFLD.
Managing obesity through lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise, along with addressing insulin resistance, is crucial for preventing and managing NAFLD effectively.
Genetics and Family History
Genetics: Certain genetic factors can predispose individuals to NAFLD. These genetic variations can influence how the body processes and stores fat, making some individuals more susceptible to developing NAFLD even without significant lifestyle factors.
Family History: Having a family history of NAFLD or related metabolic conditions increases the likelihood of developing the disease. Individuals with close relatives who have been diagnosed with NAFLD may have a higher risk themselves.
While genetics and family history cannot be changed, awareness of these factors can help individuals take proactive steps to mitigate other risk factors, such as maintaining a healthy lifestyle and regular medical check-ups, to reduce the risk and severity of NAFLD.
Symptoms of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) can often progress silently without noticeable symptoms in its early stages. However, as the disease advances, individuals may experience various symptoms, including:
Fatigue and Weakness: Persistent tiredness and lack of energy are common symptoms of NAFLD, often attributed to liver inflammation and reduced liver function.
Abdominal Pain and Discomfort: Some individuals with NAFLD may experience discomfort or dull pain in the upper right side of the abdomen, where the liver is located.
Jaundice and Yellowing of the Skin: In advanced stages of NAFLD, the accumulation of bilirubin, a yellow pigment produced by the liver, can lead to jaundice, characterized by yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes.
Swelling in the Legs and Abdomen: NAFLD can lead to fluid retention, causing swelling (edema) in the legs and abdomen. This occurs due to impaired liver function and increased pressure in the blood vessels.
Diagnosing NAFLD
Medical History and Physical Examination: Assessing medical history and conducting a physical exam to identify symptoms and signs of liver damage.
Blood Tests: Checking liver enzyme levels in the blood to assess liver function and detect inflammation or damage.
Imaging Studies: Using ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI scans to visualize the liver and detect fatty deposits or other abnormalities.
Transient Elastography (FibroScan): Measuring liver stiffness to assess fibrosis without the need for a biopsy.
Liver Biopsy: Occasionally, a small tissue sample may be taken for examination under a microscope to confirm NAFLD and assess the extent of liver damage.
Complications Associated with NAFLD
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) can lead to:
Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH): Severe liver inflammation and damage.
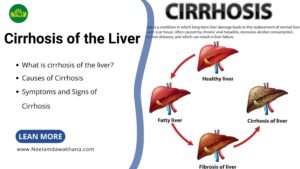
Cirrhosis: Extensive liver scarring impairing liver function.
Cardiovascular Disease: Increased risk of heart disease and stroke.
Liver Cancer: Elevated risk of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Treatment and Management of NAFLD
Lifestyle Changes: Diet and Exercise
Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limit saturated fats, sugars, and processed foods to promote liver health.
Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity for at least 30 minutes most days of the week. Include aerobic exercises like brisk walking and strength training to improve liver function and overall health.
Medications and Supplements
Medications: These may include insulin-sensitizing agents, statins, and anti-inflammatory drugs to address specific aspects of NAFLD.
Supplements: Vitamin E, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants like milk thistle may support liver health and reduce fat accumulation.
Monitoring and Follow-Up Care
Medical Check-ups: Regular visits with healthcare providers help track liver function and assess treatment effectiveness.
Liver Function Tests: Periodic blood tests monitor liver enzymes and detect any changes in liver health.
Imaging Studies: Imaging tests may be recommended to evaluate liver health and detect complications.
Weight Management: Ongoing weight management is important for reducing liver fat accumulation and improving overall health.
Medication Management: Regular reviews of medications ensure optimal treatment outcomes and minimize side effects.
Prevention Strategies for NAFLD
Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins while limiting saturated fats and sugars.
Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity for at least 30 minutes most days of the week to promote weight management and liver health.
Weight Control: Maintain a healthy weight through portion control and mindful eating habits to reduce the risk of NAFLD.
Limit Alcohol: Avoid excessive alcohol consumption to prevent liver damage and NAFLD-related complications.
Manage Chronic Conditions: Control underlying conditions like obesity, diabetes, and high blood pressure through regular medical care and lifestyle modifications.
Health Screenings: Undergo regular health check-ups to monitor liver function and detect NAFLD or related conditions early.
Conclusion
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) presents a significant health challenge globally. By adopting healthy lifestyle habits, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and weight management, individuals can reduce the risk of NAFLD and its complications. Regular monitoring, early detection, and healthcare provider guidance, alongside resources like Neelamdawakhana, are crucial for effective management. Let’s continue raising awareness and supporting prevention efforts to improve liver health and overall well-being for all.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q. Is NAFLD reversible?
A. Yes, NAFLD is reversible, especially in its early stages, with lifestyle modifications such as diet and exercise.
Q. Can NAFLD lead to liver cancer?
A. While NAFLD itself does not directly cause liver cancer, advanced stages of the disease, such as cirrhosis, increase the risk of liver cancer development.
Q. Are there any specific dietary recommendations for NAFLD?
A. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins is recommended for individuals with NAFLD. Limiting intake of saturated fats, refined carbohydrates, and sugary foods is also beneficial.
Q. Is NAFLD hereditary?
A. While genetic factors may predispose individuals to NAFLD, the condition is not solely hereditary. Environmental factors such as diet, lifestyle, and obesity also play significant roles in its development.
Q. Can NAFLD be detected without symptoms?
A. Yes, NAFLD can be detected through routine blood tests, imaging studies, or during medical evaluations even in the absence of noticeable symptoms.